
More investors are seeking ways to enter Vietnam. But they first need to understand the country and its economy before making investment decisions.
Vietnam is the 47th-largest economy in the world measured by nominal gross domestic product (GDP) and 35th by purchasing power parity (PPP), according to Wikipedia. For the past several years, Vietnam’s economic progress has gained it recognition as East Asia’s new economic tiger. Its agricultural products and petroleum industry maintain a healthy expansion in exports, and it has seen rapid growth of foreign direct investment. 2017 was a remarkable year for Vietnam, as its GDP grew 6.81%, which was above the government’s target of 6.7%.
Does this mean that now is the time to invest in Vietnam? Here are 5 reasons you should.
5 Reasons to Invest in Vietnam
- Vietnam is the 24th-largest export economy: Ever since Vietnam shifted toward a more market-oriented economy, the country has continued to expand and strive to become a leading agricultural exporter. For the past year, Vietnam experienced an outstanding rise in exports — from $176 billion in 2016 to $214 billion in 2017. Its main export partners are the US, China, Japan, South Korea and Germany. The positive net exports are a strong indicator of a growing economy. It exerts a profound influence on Vietnam’s economy by bringing in money into the country hence contributing economic growth.
- It’s a GDP top performer. Here’s Vietnam’s GDP growth per capita for the past 2 decades: *Source: Worldbank
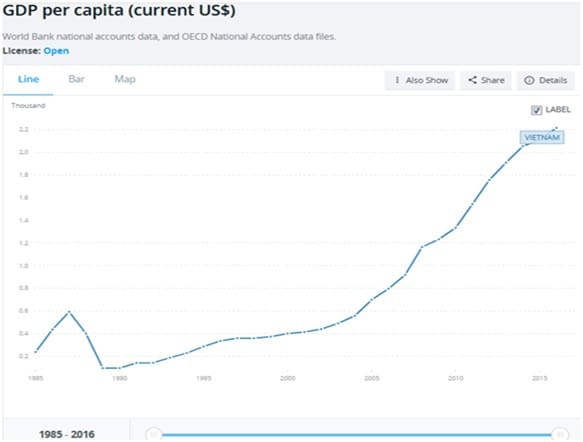
According to PricewaterhouseCoopers, a multinational audit assurance and consulting and tax services network, Vietnam could be one of the fastest growing large economies over the period to 2050. PWC estimated that the country’s GDP may grow about 5% or more per annum, while the growth of an established economy such as China may moderate to around 3-4%. *Source.
Many investors assess an investment idea/strategy based on a country’s GDP to gauge the country’s economic growth. While the market is emerging, now is the time to get in.
- Trade agreements: Vietnam has been proactively integrating with the world to establish diplomatic relations. In fact, Vietnam has bilateral agreements with the US, is a member of the World Trade Organization & ASEAN Economic Community, and, this year the European Union’s Free Trade Agreement with Vietnam (EVFTA) is expected to be signed. These trade agreements simply provide an important boost to the economy by keeping international relations that lead to creation of new markets for businesses and opportunities.
These trade agreements indicate the liberality of the market — it indicates how open Vietnam is to trading with other countries. In fact Vietnam’s prime minister recently pledged the government’s support for investors and called for their interest in Vietnam’s equitization of state-owned enterprises. He told Chairman of the EU Parliament’s International Trade Committee Bernd Lange that Vietnam considers the EU an important partner and wishes to advance comprehensive cooperation, especially in trade and investment.

- Foreign investment openness: Vietnam is progressively becoming a more open economy by encouraging more foreign investors because of its big impact on the country’s economic development. In fact, according to Prime Minister Nguyễn Xuân Phúc, Vietnam will work for the early signing of the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement, the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership to encourage foreign investors to develop and operate in the country. Potential impact of this agreement includes the following:
- Boost Vietnam’s GDP by $3.2 billion by 2020, $6.7 billion by 2025, and $7.2 billion by 2030.
- Impact Vietnam’s growth through investment and export expansion
- Vietnam’s export turnover towards the EU will gain approximately $33 billion by 2020, $42 billion by 2025, and $47 billion by 2030.
*source: Vietnam Investment Review
- Healthy FDI inflows: Vietnam’s wages are relatively lower than in China; hence, many companies from countries such as Japan, India, the US and Europe make Vietnam their manufacturing hub – that means more money coming into the country. In 2017, Vietnam’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) reached a whopping US$35.6 billion. For 2018, the country expects a breakthrough by stimulating investment in renewable energy projects, high-tech agriculture, high-value tourism services, and improved business environment by promoting skills development, particularly for modern industry and innovation.
How to Invest in Vietnam?
-
Buy ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds): According to Investopedia, the top 4 ETFs for investing in Vietnam in 2018 are: VanEck Vectors Vietnam (VNM), Guggenheim Frontier Markets (FRN), Columbia Beyond BRICs (BBRC) and iShares MSCI Frontier 100 (FM).
-
Invest in Emerging or Frontier Markets: Vietnam is one of the fastest growing economies in the world, and the investment potential for frontier and emerging markets can be a great opportunity for investors.
Vietnam is a cost-competitive country compared to China. With this, Vietnam is set to replace China as the world’s manufacturing hub. As the country positions itself to be the next manufacturing hub in the region, now is a good time to invest in financial services, logistics and courier services, telecommunications, and transport services.
